GIS Map Data Digitization Services
Data digitization is a successful method for storing data in a GIS project. The coordinates are often captured as points, lines, or polygons. It takes a long time and is expensive to digitize hard copies or scanned copies, and satellite or aerial base maps into vector data.
Simak IT Pvt. Ltd. plays a crucial role in the management of services that use digitally accurate features or maps. We have expert digitizers and staff who are adept at deciphering maps and precisely digitizing features with minimal effort.
Maps, drawings, schematics, and circuit diagrams are typically converted into digital representations via digitization services. Additionally, zonal maps, contour maps, cadastral maps, topographical maps, and utility maps also require digitization services.
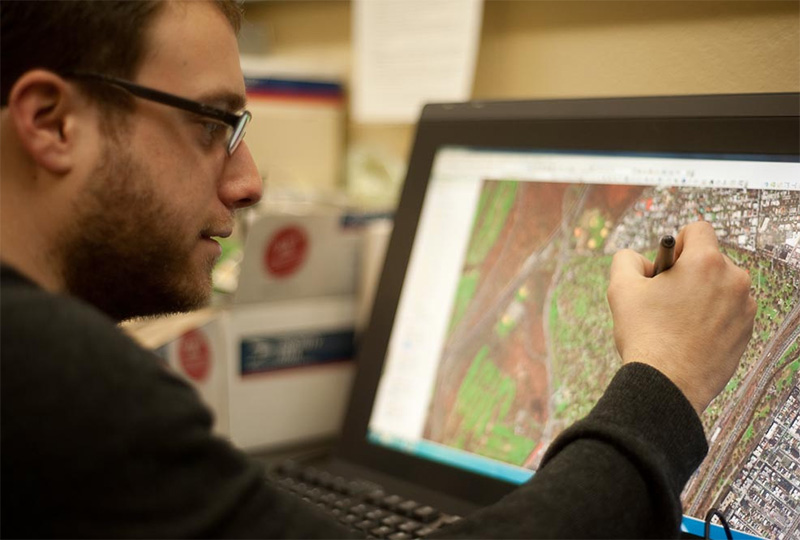

Types of GIS Map Digitization
A distinct collection of points called digitizing is used to represent an analog signal or an image. Following conversion, this data is in binary format, which a computer can read without any additional software. Text, photos, music, and video can all be converted. In contrast to the discrete digital format, analog signals are changeable. GIS data digitization comes in four different types.
Manual Digitizing
The operator makes an identical digital map on the computer by manually tracing every line on his hardcopy map. It takes a lot of time, and the precision is also subpar.
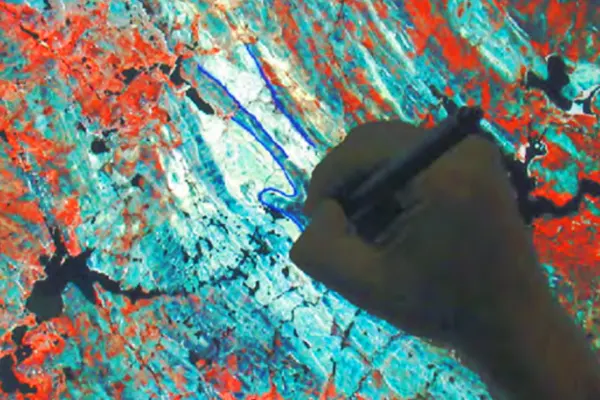

Heads-Up Digitizing
To use the technique, a computer must be used to scan a map or image. By employing high-precision digitizing software, the accuracy of the points, lines, and polygons increases.
Interactive Tracing Method
Under the operator's instruction, tracing one line at a time becomes faster and more accurate. A more advanced variant of heads-up digitizing is this technique.
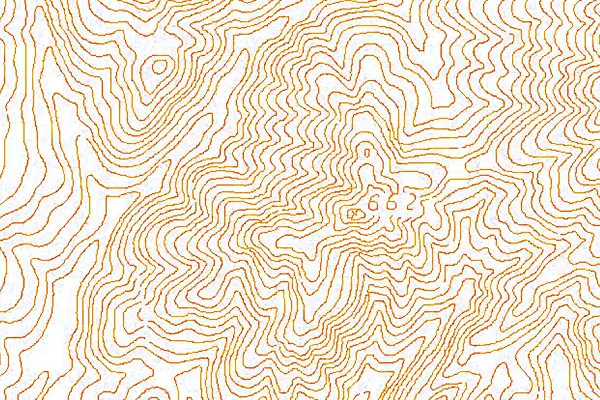

Automatic Digitizing
Automatic raster to vector conversion using pattern recognition and image processing methods. It recognizes and digitizes the features using algorithms.
Accuracy in the Data Digitization Process
The geographic precision of the characteristics is wholly dependent on the GIS database in the world of digitalization. Additionally, the quality of the digitization process ultimately determines the accuracy of the digital map. Geodetic, machine, cartographic, manuscript, positional, and attribute mistakes are among the inaccuracies found on digital maps.
Geodetic Errors
This is because the projection system was chosen in an unexpected way, which causes inaccuracy, and because poor projection causes incorrect positioning of elements on the map. As a result, the features of the digital maps do not properly overlap.
Machine Error
The digitizing tablet or the software used to digitize the pieces are to blame. It is an ingrained mistake that cannot be eliminated but can only be reduced. When converting maps from analog to digital versions, it can occasionally happen.
Cartographic Errors
It develops as a result of errors that are already present in the source map and can transfer to the digital map. One of the causes of these inaccuracies is incorrect readings or writing of the map's parts.

Manuscript Errors
It occurs based on the quality of the source maps any stretching, warping, wrinkling, or traces of folding in the original map might affect the digitization process. It could result in irregularities in the digitized features' shape, area, and coordinates.
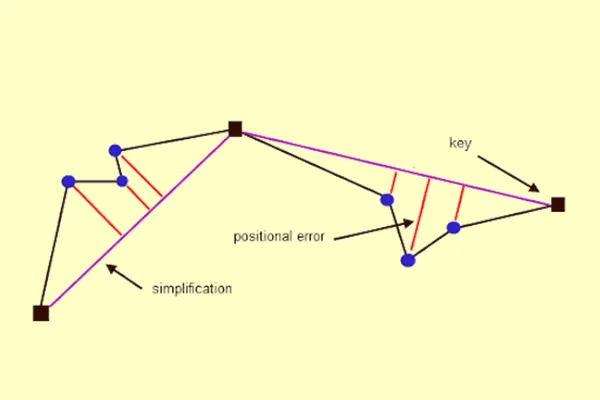
Positional Errors
This occurs when an element is improperly captured, and it can be fully fixed. Dangling Nodes, Switchbacks, knots, loops, Overshoots, Undershoots, Silvers, and Overlaps are some of the classifications for Positional Error.
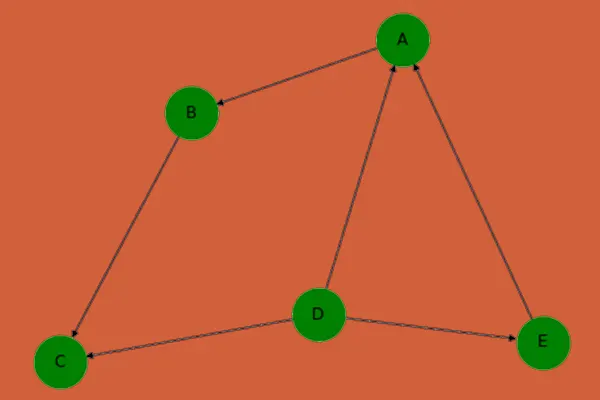
Dangling Nodes
It occurs in polygon & polyline method. With the digitized polyline, which hasn’t met, or there is any gap between the nodes where as in a digitized polygon, it happens when a polygon doesn’t connect back to it.
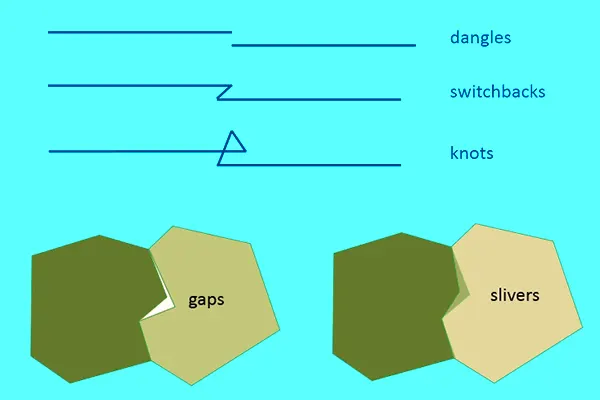
Switchbacks, Knots & Loops
A bend causes switchbacks to appear in the line, and knots and loops cause the line to fold back on itself to form a polygon. It happens because of an untrained digitizer that moves the cursor incorrectly.
As opposed to manual digitization, on-screen digitization is more common in GIS businesses. In order to digitize the feature on-screen with more accuracy, the normal resolution of the image should be scaled to the original raster data. For your forthcoming projects, consider Simak IT's error-free GIS data digitization method.
Application & Industries
We have served industries and touched lives worldwide. Changing people's lives and setting them up for a better future.